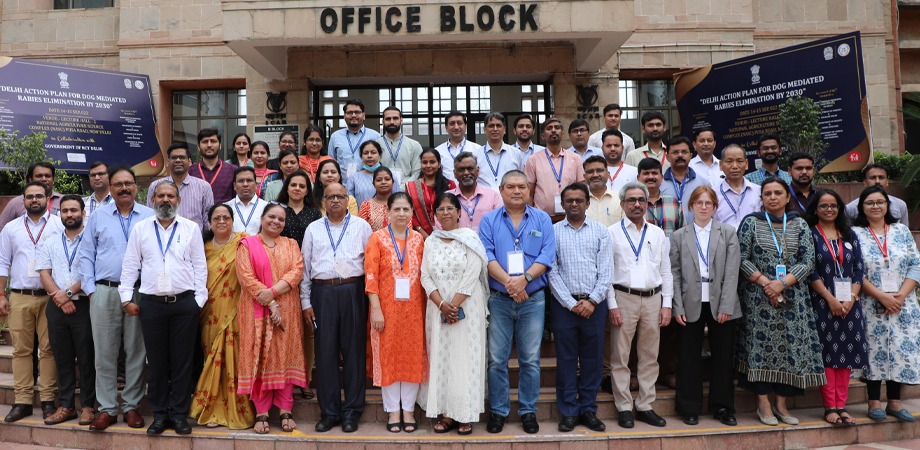
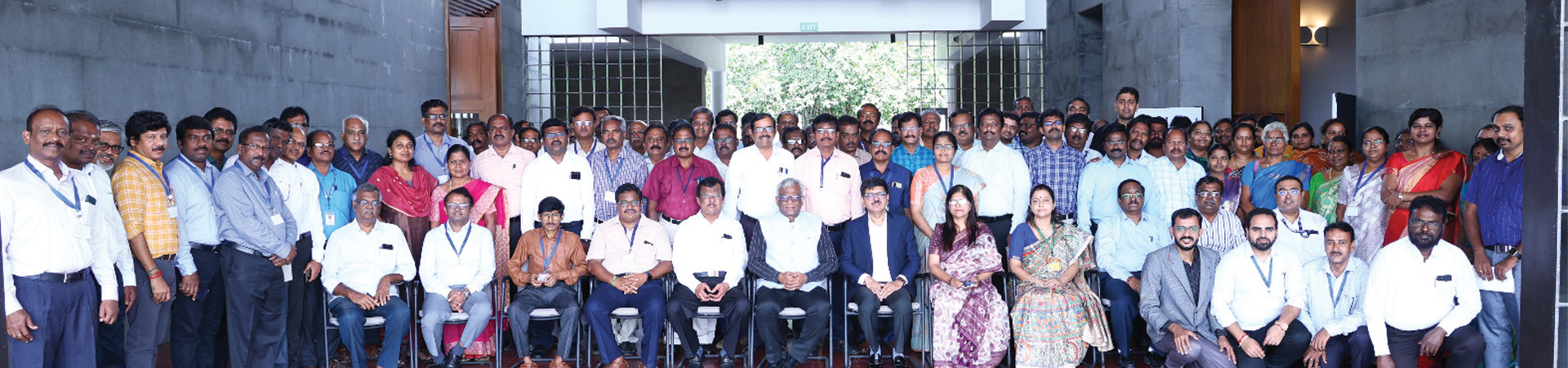
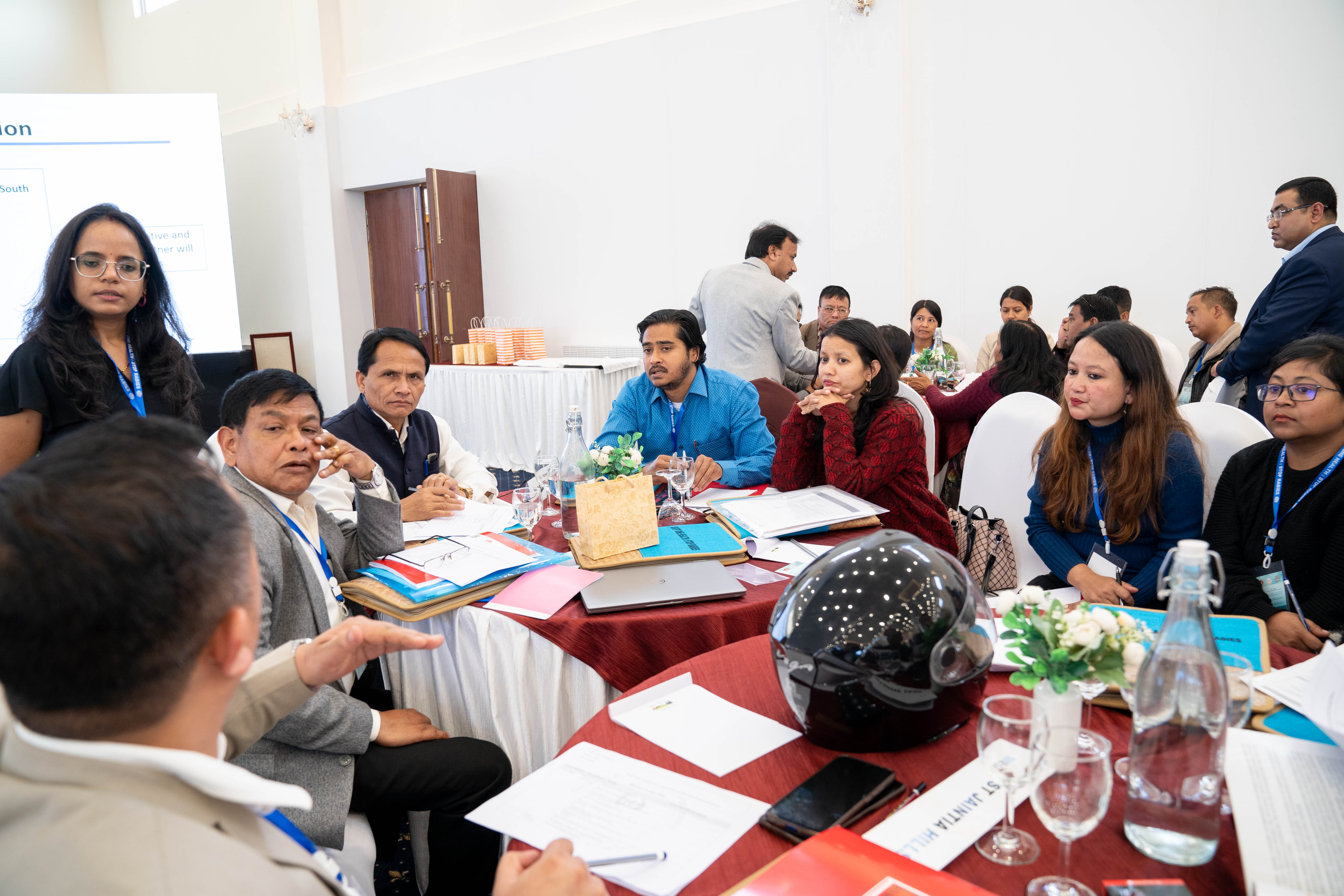
Recent Activity
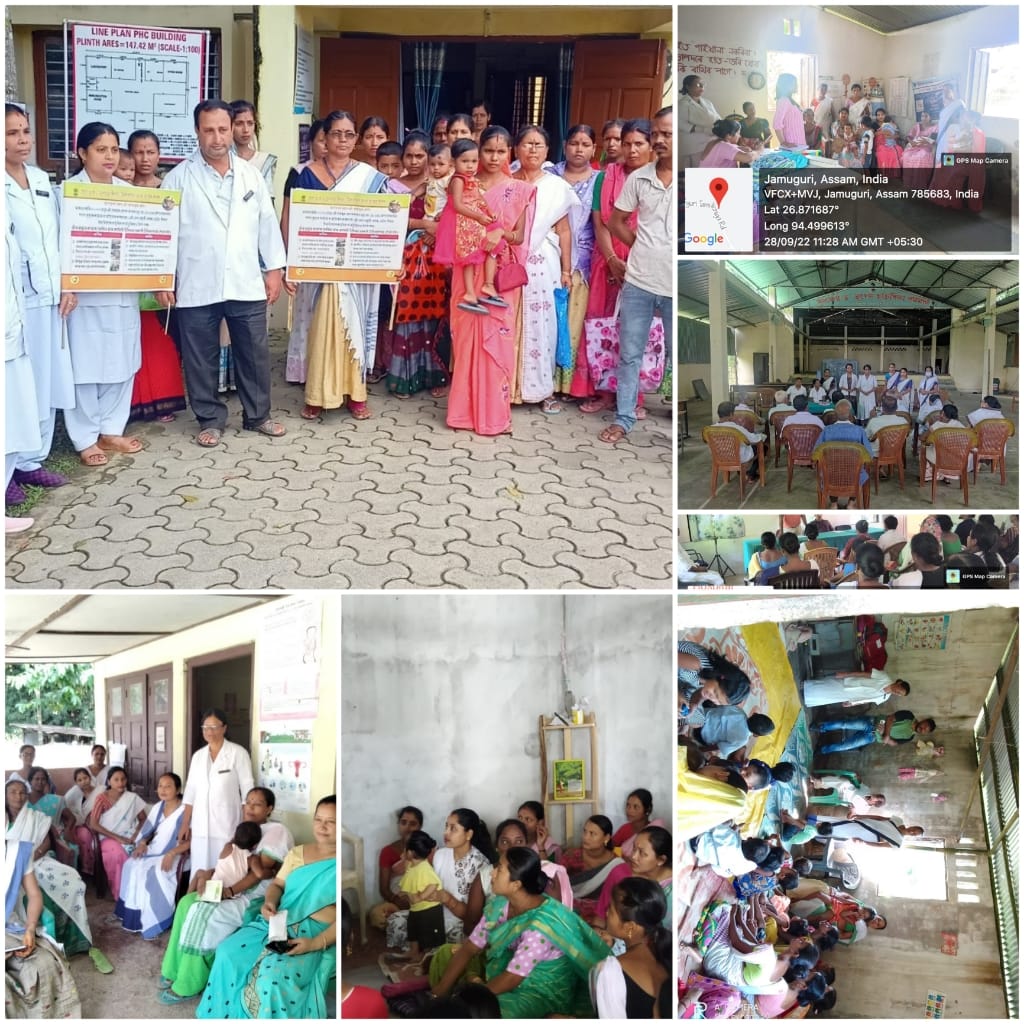
Human Health Sector Activities
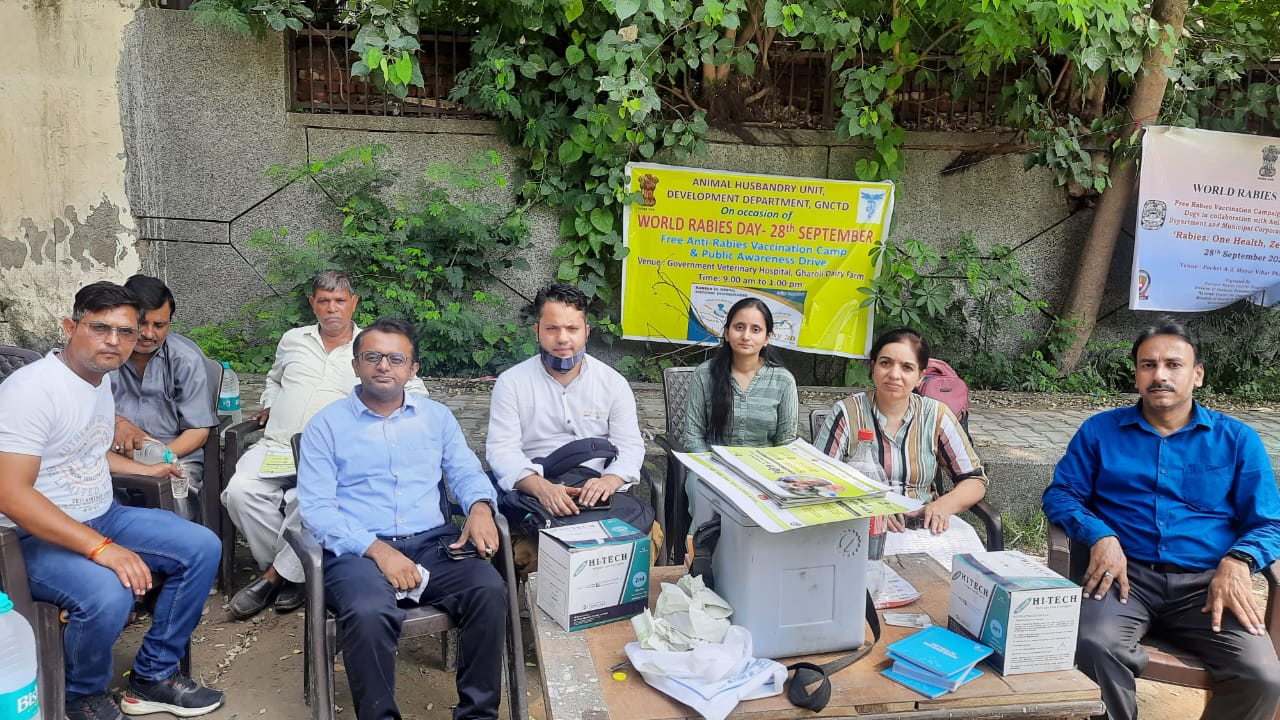
Animal Health Sector Activities
About NRCP
Rabies is responsible for extensive morbidity and mortality in India. The
disease is endemic throughout the country. Except for Andaman & Nicobar and
Lakshadweep Islands, human cases of rabies are reported from all over the
country. The cases occur throughout the year. About 96% of the mortality and
morbidity is associated with dog bites. Cats, wolf, jackal, mongoose and
monkeys are other important reservoirs of rabies in India. Bat rabies has
not been conclusively reported from the country.
Evolution of National Rabies Control Program
In the 11th five-year plan (2007–2012) Rabies control efforts in India gained momentum and the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt of India approved a “Pilot Project for the Control of Human Rabies”, for which ` 8.65 crores were allocated. For the first time, Rabies control in animals, animal birth control and vaccination of stray dogs were mentioned in this plan, as components of animal welfare to be handled by the Animal Welfare Board of India. The project was implemented by NCDC in 5 cities Delhi, Ahmedabad, Pune, Bangalore and Madurai and the project began in January 2008 and continued till 2012. The objectives of the project were prevention of human deaths due to Rabies, enhancing awareness in the general community, developing trained health manpower, strengthening diagnostic facilities, strengthening surveillance and maintenance of continuous surveillance and sensitization of other sectors. Experience gained in the pilot project indicated that strategy is feasible, reproducible, and implementable. With the lessons learned in the pilot project, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare approved National Rabies Control Programme (NRCP) in the 12th Five Year Plan for rollout in the entire country. During the 12th Five years plan, from 2014 to 2017, a small pilot was also taken to test the strategy of Animal Health Components in Haryana and Chennai through the Animal Welfare Board of India (AWBI) under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Govt of India. From 2017 onwards NCDC is coordinating to implement Human Health Component of National Rabies Control Program. From the financial year 2019-20 onwards, human health component activities at the State and District level are being funded by the National Health Mission’s program implementation and planning mechanism.
Evolution of National Rabies Control Program
In the 11th five-year plan (2007–2012) Rabies control efforts in India gained momentum and the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt of India approved a “Pilot Project for the Control of Human Rabies”, for which ` 8.65 crores were allocated. For the first time, Rabies control in animals, animal birth control and vaccination of stray dogs were mentioned in this plan, as components of animal welfare to be handled by the Animal Welfare Board of India. The project was implemented by NCDC in 5 cities Delhi, Ahmedabad, Pune, Bangalore and Madurai and the project began in January 2008 and continued till 2012. The objectives of the project were prevention of human deaths due to Rabies, enhancing awareness in the general community, developing trained health manpower, strengthening diagnostic facilities, strengthening surveillance and maintenance of continuous surveillance and sensitization of other sectors. Experience gained in the pilot project indicated that strategy is feasible, reproducible, and implementable. With the lessons learned in the pilot project, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare approved National Rabies Control Programme (NRCP) in the 12th Five Year Plan for rollout in the entire country. During the 12th Five years plan, from 2014 to 2017, a small pilot was also taken to test the strategy of Animal Health Components in Haryana and Chennai through the Animal Welfare Board of India (AWBI) under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Govt of India. From 2017 onwards NCDC is coordinating to implement Human Health Component of National Rabies Control Program. From the financial year 2019-20 onwards, human health component activities at the State and District level are being funded by the National Health Mission’s program implementation and planning mechanism.













 ( Facebook Feed )
( Facebook Feed )













Objectives:
The helpline will consist of a team of well-trained agents (Graduate and above) working on inbound and outbound processes, supervised by a Team lead. These agents will be continuously updated with crucial information required to full fill objectives of helpline.
Helpline provides a cloud-based Ticketing system with the features like- generate and resolve tickets, track complete life cycle of the ticket, Real time monitoring & tracking of the ticket, SMS notification to Caller on the ticket status, sharing of Geo location of the vaccination centers. It will also have customized reports with the real time dashboard and Data analytics to understand the pattern. An advanced auto dialer system will be implemented to auto-assign incoming calls to available agents. Helpline also has Quality control mechanism to ensure call quality and appropriate information sharing.
All queries on Rabies prevention and control will be handled by a 16*7 dedicated Rabies helpline, with a dedicated number (15400).
Same helpline also handles queries on snakebite.
Presently this helpline will serve five states: Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Assam, Puducherry, and Delhi.